Mähspitzel - Wi-Fi für Robomow

Rasenmäher
 Nachdem
wir unseren Rasenmähroboter Robomow RS615 hatten, der mit Bluetooth und einem GSM Modul ausgestattet ist,
stellte sich schnell heraus, dass damit wenig möglich ist. Per Bluetooth kann man nur in der unmittelbaren Nähe zum
Rasenmähroboter mit dem Smartphone ein paar Daten abfragen und ihn steuern. Das war's. Das
GSM Modul kann Daten nur einseitig vom Robomow zur App schicken. Mehr als
eine Info, dass er steckengeblieben ist, und eine Mähhistorie im
Nachdem
wir unseren Rasenmähroboter Robomow RS615 hatten, der mit Bluetooth und einem GSM Modul ausgestattet ist,
stellte sich schnell heraus, dass damit wenig möglich ist. Per Bluetooth kann man nur in der unmittelbaren Nähe zum
Rasenmähroboter mit dem Smartphone ein paar Daten abfragen und ihn steuern. Das war's. Das
GSM Modul kann Daten nur einseitig vom Robomow zur App schicken. Mehr als
eine Info, dass er steckengeblieben ist, und eine Mähhistorie im ![]() MyRobomow Portal gibt's aber auch
nicht. Ein bidirektionales GSM Modul gibt es erst in neueren Modellen.
MyRobomow Portal gibt's aber auch
nicht. Ein bidirektionales GSM Modul gibt es erst in neueren Modellen.
Wi-Fi
Da Robomow kein Wi-Fi Modul anbietet, habe ich
lange nach einer Lösung gesucht, den Mähroboter ins Smart Home einzubinden. Kurz bevor ich
schon dran war, ein Konkurrenzprodukt zu kaufen, habe ich das Projekt ![]() Mähspitzel
gefunden. Mit einem
Mähspitzel
gefunden. Mit einem ![]() WEMOS LOLIN D32 Pro
wird eine Verbindung per Bluetooth mit dem Robomow hergestellt und
per Wi-Fi mit dem heimischen Netzwerk. Somit kann man den Robomow wie mit
der App von überall steuern und zudem wichtige Infos abfragen. Mit etwas Geschick kann man den
programmierten Rasenschnitt pausieren, wenn es gerade geregnet hat oder Regen angekündigt ist.
Auch den Zeitpunkt des nächsten Ausfahrens kann man abfragen und somit z. B. vorher die
Garage öffnen oder eben nicht.
WEMOS LOLIN D32 Pro
wird eine Verbindung per Bluetooth mit dem Robomow hergestellt und
per Wi-Fi mit dem heimischen Netzwerk. Somit kann man den Robomow wie mit
der App von überall steuern und zudem wichtige Infos abfragen. Mit etwas Geschick kann man den
programmierten Rasenschnitt pausieren, wenn es gerade geregnet hat oder Regen angekündigt ist.
Auch den Zeitpunkt des nächsten Ausfahrens kann man abfragen und somit z. B. vorher die
Garage öffnen oder eben nicht.
Material
| Stück | Bezeichnung | Bezugsquelle | Preis |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Wemos Lolin D32 Pro | eBay | 20 € |
| 1 | DC-DC Wandler | Amazon/eBay | 5 € |
| 1 | GPS-Modul GYGPSV5 (optional) | eBay | 25 € |
| 1 | JST 2.0 mm 2-poliger Stecker mit Kabel | Amazon/eBay | 5 € |
| 1 | XT60 Stecker & XT60E Buchse | Amazon/eBay | 10 € |
| 1 | Gehäuse Hammond 1591ATCL | voelkner | 5 € |
| 1 | IPEX Buchse | eBay | 3 € |
| 1 | 2,4 Ghz WLAN Antenne SMA Pigtail auf IPEX | eBay | 4 € |
| 1 | Robomow RS mit Firmware 2.82 bis 2.90 | sollte vorhanden sein | |
| 1 | Robomow RC mit Firmware 1.79 bis 2.029 | sollte vorhanden sein | |
| 77 € | |||
Hardware
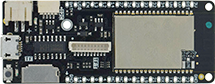
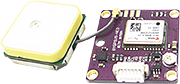
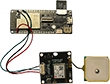


 Wenn
man das GPS Modul nutzen möchte,
verbindet man die Kontakte wie folgt:
Wenn
man das GPS Modul nutzen möchte,
verbindet man die Kontakte wie folgt:
Wemos GND ▸ GPS GND
Wemos 3V ▸ GPS VCC
Wemos DIO 22 ▸ GPS TX
Nun nimmt man die obere Abdeckung des Robomow ab. Eine Videoanleitung ist unten in den Links zu
finden. Den DC-DC Wandler verbindet man am Eingang mit dem Akku des Robomow. Leider konnte ich keine
Bezugsquelle für Stecker und Buchse der Robomow Verbindung am Akku finden und musste das Kabel
an den verbauten Stecker anlöten. Den Ausgang des DC-DC Wandlers führt man mit einem Kabel
durch eines der länglichen Löcher in der abgenommenen Haube des Robomow. Dort habe ich
einen XT60 Stecker angelötet. Nun stellt man den DC-DC Wandler mit einem Multimeter auf einen
Wert zwischen 3,3V und 3,7V ein und fixiert dies mit Schraubensicherungslack. Zum Testen kann man
auch einfach eine Powerbank mit dem Micro-USB Eingang des Wemos verbinden. Ins Gehäuse bohrt
und feilt man ein Loch für die XT60e Buchse und fixiert diese mit zwei 2,5 mm Schrauben.
Die Buchse verbindet man mit dem JST 2.0 mm Stecker, den man dann in den Batterieeingang des
Wemos steckt. Nachdem das Gehäuse verschlossen ist, findet es unter der Klappe oben am Robomow
seinen Platz.
Antenne



 Wenn
die interne Antenne auf der Platine nicht ausreicht, damit der Mähspitzel im gesamten Garten
mit dem Wi-Fi verbunden bleibt, kann man eine externe Antenne
anschließen. Da auf der Platine leider die hierfür notwendige IPEX Buchse fehlt, muss man
diese zunächst anlöten. Danach entfernt man den Widerstand R15 und lötet ihn bei R14
ein oder verbindet einfach die beiden Lötpunkte R14. Danach kann man mit einem IPEX auf SMA
Kabel eine 2,4 GHz Wi-Fi Antenne anschließen. Der Materialwert liegt
bei unter €10.
Wenn
die interne Antenne auf der Platine nicht ausreicht, damit der Mähspitzel im gesamten Garten
mit dem Wi-Fi verbunden bleibt, kann man eine externe Antenne
anschließen. Da auf der Platine leider die hierfür notwendige IPEX Buchse fehlt, muss man
diese zunächst anlöten. Danach entfernt man den Widerstand R15 und lötet ihn bei R14
ein oder verbindet einfach die beiden Lötpunkte R14. Danach kann man mit einem IPEX auf SMA
Kabel eine 2,4 GHz Wi-Fi Antenne anschließen. Der Materialwert liegt
bei unter €10.
Software
Mittels USB-Kabel ist das ESP32 Board mit dem Computer zu verbinden.
Unter Werkzeuge der Arduino IDE sind folgende Parameter einzustellen:
- Board: LOLIN D32 PRO
- Upload Speed: 921600
- Flash Frequency: 80MHz
- Partition Scheme: Minimal SPIFFS (Large APPS with OTA)
- Core Debug Level: Keine
- PSRAM: Enabled
- Port : <Anschluss, mit dem der Wemos verbunden ist>
Nach dem Öffnen des Sketches mspitzelAPconnect.ino die Informationen im Quellcode
beachten und SSID & Passwort des heimischen Netzwerks einstellen sowie die Zugangsdaten zur
Bedienoberfläche des Mähspitzels. Nun den WLAN-Loader auf den ESP32 hochladen. Wenn das
nicht funktioniert, ist eventuell der ![]() Wemos Treiber nicht
installiert. Danach sucht man im LAN nach dem neuen WLAN Gerät und ruft dessen Oberfläche
auf mit http://IP-Adresse:8080. Anschließend wählt man die Datei
mspitzel.ino.d32_pro.bin aus und führt das Update durch. Bei erfolgreichem Upload und
Neustart ist Mähspitzel unter http://IP-Adresse erreichbar. Falls nicht verändert, ist als
Nutzername Mspitzel und als Passwort Mspitzel007 einzutragen. Spätere
Aktualisierungen können mit http://IP-Adresse:8080 durchgeführt werden, wobei keine
Programmeinstellungen verloren gehen.
Wemos Treiber nicht
installiert. Danach sucht man im LAN nach dem neuen WLAN Gerät und ruft dessen Oberfläche
auf mit http://IP-Adresse:8080. Anschließend wählt man die Datei
mspitzel.ino.d32_pro.bin aus und führt das Update durch. Bei erfolgreichem Upload und
Neustart ist Mähspitzel unter http://IP-Adresse erreichbar. Falls nicht verändert, ist als
Nutzername Mspitzel und als Passwort Mspitzel007 einzutragen. Spätere
Aktualisierungen können mit http://IP-Adresse:8080 durchgeführt werden, wobei keine
Programmeinstellungen verloren gehen.
Verbinden
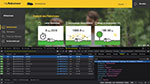 Im
Reiter Konfiguration sind die Mäherdaten zu setzen. Die IMSI ist der
Bluetooth-Name des Robomow, der z.B. im Smartphone steht, wenn man die App mit
dem Robomow verbunden hat. Sie lautet Mo0000, wobei statt der Nullen eine Zahl
steht. Die vier Ziffern sind übrigens auch die letzten vier Ziffern der
Seriennummer. Darunter ist die Mainboard-Seriennummer einzutragen, die man
Im
Reiter Konfiguration sind die Mäherdaten zu setzen. Die IMSI ist der
Bluetooth-Name des Robomow, der z.B. im Smartphone steht, wenn man die App mit
dem Robomow verbunden hat. Sie lautet Mo0000, wobei statt der Nullen eine Zahl
steht. Die vier Ziffern sind übrigens auch die letzten vier Ziffern der
Seriennummer. Darunter ist die Mainboard-Seriennummer einzutragen, die man ![]() hier abfragen
kann. Funktioniert dies nicht über die Seite, so kann man z. B. in
Firefox mit F12 die Werkzeuge für Web-Entwickler öffnen und
sich dann bei
hier abfragen
kann. Funktioniert dies nicht über die Seite, so kann man z. B. in
Firefox mit F12 die Werkzeuge für Web-Entwickler öffnen und
sich dann bei ![]() MyRobomow anmelden.
Danach kann man im Debugging-Fenster im Bereich Netzwerkanalyse ▸
Antwort oben links nach products suchen und danach ganz rechts im
Antwort-Fenster das JSON-Objekt mit einem Klick auf das kleine weiße Dreieck
aufklappen. Dort kann man die MainboardSerial ablesen. Siehe Screenshot.
Danach stellt man auf der Startseite BLE von Aus auf Ein. Es ändern
sich die Farben der Auswahlliste:
MyRobomow anmelden.
Danach kann man im Debugging-Fenster im Bereich Netzwerkanalyse ▸
Antwort oben links nach products suchen und danach ganz rechts im
Antwort-Fenster das JSON-Objekt mit einem Klick auf das kleine weiße Dreieck
aufklappen. Dort kann man die MainboardSerial ablesen. Siehe Screenshot.
Danach stellt man auf der Startseite BLE von Aus auf Ein. Es ändern
sich die Farben der Auswahlliste:
Blau ▸ Nach eingetragenem Bluetooth-Gerät wird gesucht
Gelb/Orange ▸ Versuch eines Verbindungsaufbaus
Grün ▸ Mähspitzel ist mit dem Mäher verbunden
Reiter Konfiguration
Auch wenn dies der letzte Reiter ist, sollte er zuerst
aufgerufen werden, da hier die Grundeinstellungen zu treffen sind, damit überhaupt etwas passiert.
Wi-Fi
Hier stehen die Zugangsdaten zum Wi-Fi zu Hause. Bei WLAN-Mesh wechselt der
ESP32 nicht automatisch zu einem besseren Access Point. Mit Unterschreitung der eingestellten
Feldstärke unter Neu verbindenwird daher eine Neuverbindung zum Access Point
erzwungen. Empfehlenswert ist ein Wert von -79 dBm. Der Wert ist jedoch von der lokalen
Anordnung der Access Points abhängig.
Sende Kommando zum Mäher
Ohne Aktivierung können keine Mäher-Einstellungen geändert werden.
Ereignisprotokoll
Hier kann das Ereignisprotokoll heruntergeladen werden. Je nach Protokollgröße kann dies
sehr lange dauern. Daher sollten die Protokolle regelmäßig gelöscht werden.
pushbullet Benachrichtigung
Google Werkzeug zur Push-Benachrichtigung für Android
Smartphones. Mehr Infos zu ![]() Pushbullet
Pushbullet
google maps Robot Position
Zur Anzeige der Position das Mähroboters in der Google Maps Karte, muss man sich wie folgt
kostenfrei einen Google Maps API Key erstellen.
- Auf der
 Google Maps Entwickler Website einloggen und auf auf Jetzt starten klicken.
Google Maps Entwickler Website einloggen und auf auf Jetzt starten klicken. - In Schritt (1) ein Abrechnungskonto erstellen. Hier den Bedingungen zustimmen, mit dem per SMS zugesandten Code bestätigen, kostenlose Testversion starten anklicken und seine Identität per Kreditkarte und Personalausweis bestätigen.
- In Schritt (2) ein Projekt erstellen und sinnvoll benennen.
- In Schritt (3) die benötigte Maps JavaScript API wählen und aktivieren.
- In Schritt (4) den API Schlüssel für Web > Maps Javascript API anfordern. Hierzu auf der Anmeldedaten-Seite oben auf +Anmeldedaten erstellen klicken und API Key wählen.
- Der erzeugte API Key wird jetzt angezeigt und muss in der Mähspitzel-Konfiguration eingefügt werden.
- In der Google Cloud Platform oben links auf das Hamburgermenü > Abrechnung gehen und das erzeugte Rechnungskonto mit dem Projekt verknüpfen.
- Zum Testen im Reiter Mäher-Status&GPS oben auf EchtzeitRobot Position klicken. Die Position sollte nun in Google Maps angezeigt werden. Wenn dort noch For development purposes only steht, wurden die Zahlungsinformationen noch nicht abschießend durch Google geprüft.
BLE automatisch Ein/Aus
Zum Stromsparen kann man die Bluetooth Verbindung zwischen Mähspitzel und dem Robomow für
Zeiten deaktivieren, in denen diese nicht benötigt wird. Empfohlen sind 2 Minuten für
Ein vor EinsatzAkkuladung größer/gleich.
Zusatzfunktionen
Wird an der Platine an DIO 15 etwas angeschlossen, kann über diesen Konfigurationspunkt
der Digitale Ausgang ein- oder ausgeschaltet werden. Bei Ein liegt am Pin eine Spannung von
ca. 3,3V an. Bei Aus ist dieser auf logisch 0. Es gibt keine Abhängigkeiten zu BLE Ein/Aus oder zur
inaktiven Zeit. Somit kann jeder nach Bedarf diesen verwenden, bzw. eigene Abhängigkeiten
programmieren.
Benachrichtigungsereignisse
Die hier eingegebenen Nummern werden gemeldet. Zum Test kann
2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,24,32,33,41,42,45,46,47,49,56,61,62,63,64,65,66,68,74,75,250
eingestellt werden. Die Bedeutung der "Stop Reasons" ist wie folgt:
| Nr. | LCD Message | Description | Extra information |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | No message | STOP button is pressed | |
| 2 | No wire signal | No wire signal is detected during the automatic operation warming up phase | |
| 3 | Start inside/change wires in plot connector | Automatic operation was initiated by the user while robot is outside the plot | |
| 4 | Key pressed | Button constant press is detected during the automatic operation warming up phase. | Occurs only if operation was initiated by the user and not automatically. |
| 5 | Bumper pressed | Bumper is detected during the automatic operation warming up phase. | Occurs only if operation was initiated by the user and not automatically. |
| 6 | Front wheel problem | Front wheel dropoff is detected during the automatic operation warming up phase. | Occurs only if operation was initiated by the user and not automatically. |
| 7 | Stuck in place/Cross outside | Consecutive turn movements are received without any heading movements | one of the following occurred: 1) More than 35 in place turns movement occurred without forward movements 2) more than 90 seconds have elapsed since the last time robot was moving in forward direction |
| 8 | Stuck in place | Robot is performing forward legs without receiving any termination event | robot performed more than 2 legs that ended due to distance limit (250 meter) |
| 9 | Check power | Robot got off the base station because charging voltage is not detected | if charging voltage is lost when robot is charging in the base station then after 5 minutes in case battery is in recharge state or 60 minutes in all other cases robot will get off the base station and wait for wire signal detection which indicates power is back on and we can return to the base station |
| 10 | No message | Charging process is halted because no charging voltage is detected | if charging voltage is lost when robot is charging then after 5 minutes in case battery is in recharge state or 60 minutes in all other cases robot will stop charging and recoed this event |
| 11 | No message | we are during the one time setup and we stopped the automatic operation since either the base position test stage or the wire test stage ended | |
| 12 | No message | we are during the one time setup and we stopped the automatic operation in order to handle an obstacle event | |
| 13 | Drive overheat | Drive driver overheat is detected | |
| 14 | Base problem | Robot was charging in the base, the due to power break it disconnected from the base in order to display the problem and failed to connect to the base station for more than 3 times | |
| 15 | Recharge battery | Battery state indicates automatic operation cannot be performed | Occurs during the automatic operation warming up phase only if operation was initiated by the user and not automatically. |
| 16 | Drive overheat | Drive driver overheat is detected | we tried to recover from this state without success and too much time have elapsed and eventually we decided to terminate the operation |
| 17 | Recharge battery | Battery voltage indicates its time to stop the automatic operation and go to the base station (if exists) | |
| 18 | Recharge battery | Battery voltage indicates its time to stop the automatic operation | |
| 19 | No message | Charging process is halted because charger overheat is detected | |
| 20 | No message | Carrying handle is lifted during automatic operation | if stop button is partially pressed or pressed slowly we can also receive this stop reason |
| 21 | Handle lifted | Carrying handle is lifted during the automatic operation warming up phase. | Occurs only if operation was initiated by the user and not automatically. |
| 22 | Start elsewhere | Drive over-current is detected during automatic operation | Occurs only if robot is during scan operation after 10 drive overcurrent events are detected |
| 23 | Start elsewhere | Drive over-current is detected during manual operation | |
| 24 | Stuck in place | Multiple robot Slippage events are detected. | More than 10 consecutive slippage events occurred |
| 25 | Switch off before lifting | Tilt is detected | Tilt is detected for more than 5 seconds |
| 26 | No message | System switch is switched off | |
| 27 | Mow overheat | Mow overheat is detected during automatic operation | |
| 28 | Check mow height | Mow over-current is detected during automatic operation | Occurs only if we are not in mow eco mode |
| 29 | Check mow height | Mow over-current is detected during remote control operation | |
| 30 | No wire signal | Wire signal is not detected during automatic operation | |
| 31 | Mow overheat | Mow overheat is detected during manual operation | |
| 32 | Cross outside | Wire escape is detected during automatic operation | If the following exists for more than 20 seconds: -operation we are during automatic operation -operation all wire sensors are out -operation drive motors are active |
| 33 | Front wheel problem | Front wheel dropoff detected for a long time during automatic operation | Front wheel dropoff is detected for more than 15 seconds during scan Or Front wheel dropoff is detected for more than 35 sec during automatic operation (Edge/Scan) |
| 34 | Inactive Time | Inactive time detected during automatic operation | Occurs only if operation was initiated automatically and not by the user. |
| 35 | Time Completed | We reached the required mowing time in the current active zone | Occurs only if the following exists: - operation was initiated automatically and not by the user - we are not during demo mode |
| 36 | Rain detected | Rain is detected during automatic operation. | Occurs only if operation was initiated automatically and not by the user. |
| 37 | No message | We are during the BIT edge terminate test and end of edge is detected | |
| 38 | No message | Remote control Safety button is pressed during automatic operation | |
| 39 | No message | stop button is pressed during manual operation | |
| 40 | Rain detected | docking station automatic departure is disabled due to rain detection | |
| 41 | No message | Automatic operation was stopped and robot is sent to search for the base station since front wheel dropoff was detected for too long. | Occurs only if Base exists. This is for the safety standard requirement |
| 42 | Front wheel prob | Automatic operation was stopped since front wheel dropoff was detected for too long. | Occurs only if Base does not exists. This is for the safety standard requirement |
| 43 | No message | Automatic operation was stopped and robot is sent to search for the base station since bumper was detected for too long. | Occurs only if Base exists. This is for the safety standard requirement |
| 44 | Bumper pressed | Automatic operation was stopped since bumper was detected for too long. | Occurs only if Base does not exists. This is for the safety standard requirement |
| 45 | Drive overheat | Drive driver overheat is detected during automatic operation but operation is not yet stopped and robot is trying to recover from it. |
|
| 46 | Mow overheat | Mow overheat is detected during automatic operation but operation is not yet stopped and robot is trying to recover from it. | |
| 47 | No wire signal | No wire signal is detected during automatic operation but operation is not yet stopped and robot is trying to recover from it. | |
| 48 | |||
| 49 | No message | wrong menu place is detected during automatic operation | this should not occure and was entered as an extra protection |
| 50 | Recharge battery | battery discharge time limitation is detected which indicates its time to stop the automatic operation and go to the base station (if exists) | we limit the operation time according to the battery capacity in order to protect the battery liftime |
| 51 | Recharge battery | battery discharge time limitation is detected during the automatic operation warming up phase. | Occurs only if operation was initiated by the user and not automatically. we limit the operation time according to the battery capacity in order to protect the battery liftime |
| 52 | Recharge battery | Battery voltage indicates its time to stop the automatic operation and go to the base station (if exists) | this occurs due to battery voltage drop monitor detection. this monitor searches for voltage drop in any one of the battery cells which indicates battery needs to be recharged |
| 53 | Recharge battery | Battery capacity indicates its time to stop the automatic operation and go to the base station (if exists) | |
| 54 | Recharge battery | user tries to send the robot to the base station but battery state does not allow it | |
| 55 | Recharge battery | Battery capacity indicates its time to stop the automatic operation | |
| 56 | No message | We are during the BITedeg near wire test and end of edge is detected | |
| 57 | No message | robot panel CANCEL button is pressed during automatic operation - "panic" mode | CANCEL button was pressed for more than 300 ms |
| 58 | Operation Shorter Then Expected | docking station automatic departure is disabled due to short time operation cycle detections | 10 conseqenceal automatic operation that were less then 15 minutes were perfromed |
| 59 | Low Temperature | docking station automatic departure is disabled due to low temperature | Occurs only if operation was not initiated by the user and was initiated from the docking station |
| 60 | Check mow | Mow over-current or Mow disconnection is detected during automatic operation warming up phase while the robot is in the docking station | |
| 61 | Stuck In Place | robot is stuck on the wire. | 5 rescue behavior retries were performed but without success. |
| 62 | Bumper pressed | Automatic operation was stopped since bumper was detected for too long. | Occurs only if Base exists. This is for the safety standard requirement |
| 63 | Stuck In Place | robot is stuck in place without the ability to move the motors for more than 100 seconds. | this can accur for example due to bumper which is not released and robot constantly detects it |
| 64 | Stuck In Place | robot is trapped and performed more than 100 consecutive short legs (legs with distance shorter then 150cm) | such scenarios can happen for example when robot gets trapped in a certain area where it is surrounded by many obstacles |
| 65 | Floater Problem | floater motor driver problem is detected | |
| 66 | Base Problem | we reached maximal edge quarters while performing wire following | |
| 67 | No message | Docking station is detected during go to entry point process | during search for entry point the docking station is detected. This could indicate a problem since the docking station should not be detected when going to another subzone |
| 68 | No message | battery overheat is detected during charging | battery temperature is higher than 60 degrees |
| 69 | No message | robot panel UP button is pressed during automatic operation - "panic" mode | UP button was pressed for more than 300 ms |
| 70 | No message | robot panel DOWN button is pressed during automatic operation - "panic" mode | DOWN button was pressed for more than 300 ms |
| 71 | No message | a command to stop the robot was received from the robomow mobile application | |
| 72 | Start elsewhere | Drive over-current is detected during automatic operation | Occurs only if robot is during scan operation after 5 drive overcurrent events are detected |
| 73 | No message | Charging operation was stopped in order to send a robot operation GSM message | |
| 74 | Drive overheat | Drive motor overheat is detected | we tried to recover from this state without success and too much time have elapsed and eventually we decided to terminate the operation |
| 75 | Drive overheat | Drive motor overheat is detected during automatic operation but operation is not yet stopped and robot is trying to recover from it. |
|
| 76 | Rain detected | Rain is detected during automatic operation. | Occurs only if operation was initiated automatically and not by the user. |
| 77 | No message | Battery capacity timeout | battery is not being charged good and does not reach the required cells state also after charging for a long time (more than 30 hours). |
| 200- 255 | Failure: # | Will be received when system failure is detected. |
Reiter Einstellungen
Um zu prüfen, ob ein Setzen der
gewünschten Einstellung erfolgreich war, muss man diese Seite erneut aufrufen.
Inaktive Tage / Inaktive Zeit
WICHTIG – Sind weniger als 6 Tage aktiv oder die aktiven Tage/Zeiten ungünstig aufgeteilt, so
verlängern sich die Bluetooth-Antwortzeiten vom Mäher deutlich. Im ungünstigen Fall wird
dadurch die Bluetooth-Verbindung immer wieder neu aufgebaut und unter Umständen z.B. die
Webseite Mäher-Einstellungen nicht oder nur unvollständig aktualisiert. Ein Setzen der
Einstellungen ist dann kaum möglich, bzw. wird einfach nicht durchgeführt und muss
mehrfach wiederholt werden. Dies ist auch mit der Robomow-App nachvollziehbar.
Automatikbetrieb - Wochenprogramm
Aus - Schaltet alle Zonen, einschließlich Zonen A und B, aus.
Ein – Alle Zonen, außer Zone A, Zone B und Nebenzone 4, werden eingeschaltet.
Erkenne Basisstation - Suchkapazität und Suchspannung
Wer diese Werte ändern will, sollte sich mit dem eingebauten Akkutyp sehr gut auskennen oder
die Finger davon lassen.
Drehrichtung Messer Automatisch
Wird ausschließlich durch den Mähspitzel gesteuert. Eine ständige
Bluetooth-Verbindung ist erforderlich. Die Drehrichtung wird nach jeden Mäheinsatz ab
20 Minuten Mähdauer in der Fläche geändert.
Reiter Telemetrie
Hier wird der Zustand des Akkus angezeigt. Dieser enthält 8 Zellen. Die Werte jeder einzelnen Zelle werden hier angezeigt. So kann man sehen, ob ggf. eine Zelle defekt ist und – sofern man technisch versiert genug ist – diese eine Zelle austauschen. Die Telemetrie-Daten alle 1,2 Sekunden zyklisch abgefragt. Nur, wenn der Mäher im Einsatz ist, erfolgt bei manchen Werten die korrekte Anzeige. Eine Änderung des Status Neigung, Beschleunigungssensor erfolgt erst nach starkem und langem Ankippen des Mähers. Ähnlich verhält es sich mit dem Status der Stoßstange. Beim RS-Modell muss man diese sogar lange manuell drücken. Mit Klick auf die Überschrift Akku Zellspannungen kann man sich hierzu auch eine grafische Auswertung anzeigen lassen. Es erfolgt dort keine automatische Aktualisierung, sodass man die Seite im Browser gegebenenfalls neu laden muss. Mit Anklicken von Zelle x in der Legende lassen sich einzelne Kurven aus- bzw. einblenden. Die Grafik wird mittels aktiver Internetverbindung nach Google LineChart generiert. Für die sachlich richtige Interpretierung der Grafik sind grundlegende Kenntnisse von LiPo-Akkus erforderlich.
Reiter Status&GPS
Wurden durch das optionale GPS-Modul ausreichend
Satelliten gefunden, so werden aktuelle Mäher-Position und ein Link auf der obersten Zeile
eingeblendet.
Einsatzprotokoll
Das Einsatzprotokoll wird im EEPROM gespeichert. Maximal 189 Einträge sind im programmierten
Ringspeicher möglich. Danach wird das älteste Ereignis durch das neueste
überschrieben.
Telnet
Beim Zugriff auf den Mähspitzel per Telnet (Port 23) sind folgende
Befehle möglich:
? - 3 Sekunden auflisten der möglichen Anweisungen
Q - Neustart Mähspitzel
F - Rücksetzen der Konfiguration & Neustart
Z - Lösche letzte Zeile Ereignisprotokoll
L - Lösche Ereignisprotokoll
N - Testbenachrichtigung versenden
Icon
Wer möchte, kann sich noch ein Icon auf die SD-Karte speichern, das
im Browser-Tab, der Lesezeichenleiste und auf dem Home-Screen das Smartphones angezeigt wird.
Hierzu eine geeignete PNG Datei mit http://
- favicon.png
- android-chrome.png
- apple-touch-icon.png
Automatisierung
Wer den Mähspitzel ins Smart Home einbinden möchte,
kann vieles als JSON abfragen. Folgende Seiten können durch Anhängen an die URL abgefragt
werden:
/setcfg - Setzen der Konfiguration
/setcmds - Setzen aller anderen Kommandos/Einstellungen
/show_robot_map - Anzeigen der Google Map
/dump - zur Fehleranalyse
/renewtelem - für Telemetrie (json)
/oncetable - Tabelle für batterychart (json)
/renew - für Start (json)
/once - für Einstellungen (json)
/oncemisc - für Status&GPS Tabellen ohne GPS-Daten (json)
/console - für alle Webseiten freier Speicher und GPS-Daten (json)
/copyfav - zum Hochladen der FavIcons
Ein Beispiel für eine Home Assistant Implementierung ist unter den Downloads zu
finden.